Jun 10, 18 · It is usually expressed as a ratio of two integers For example an odds of 01 is written as 110 and an odds of 5 is written as 51 Risk and risk ratios are more commonly used than odds and odds ratios in medicine as these are much more intuitive Risk describes the probability of an event occurringThe odds ratio can also be used to determine whether a particular exposure is a risk factor for a particular outcome, and to compare the magnitude of various risk factors for that outcome OR=1 Exposure does not affect odds of outcome OR>1 Exposure associated with higher odds of outcome OROct 01, 07 · Relative measures of effect are risk ratio (ie the ratio between two incidence proportions), incidence rate ratio (the ratio between two incidence rates), and OR (the ratio between two odds) The risk difference is an absolute measure of effect (ie the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals minus the risk of the same outcome in unexposed)

The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
Odds ratio vs relative risk vs hazard ratio
Odds ratio vs relative risk vs hazard ratio-RR and OR are commonly used measures of association in observational studies In this video I will discuss how to interpret them and how to apply them to patThe risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions


Tips For Teachers Of Evidence Based Medicine Understanding Odds Ratios And Their Relationship To Risk Ratios Springerlink
Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a rApr 21, 21 · The ratio of these is the risk ratio, a relative measure of association Risk Ratio = CI e /CI u = 090/058 = 155 Interpretation Smokers had 155 times the risk of respiratory disease compared to nonsmokers over an 18 year period of observation Using the same cumulative incidences we can calculate the risk difference, an absolute measureAug 16, 18 · For estimates of odds ratios, this is logit (ie the logarithm of the odds of the mean);
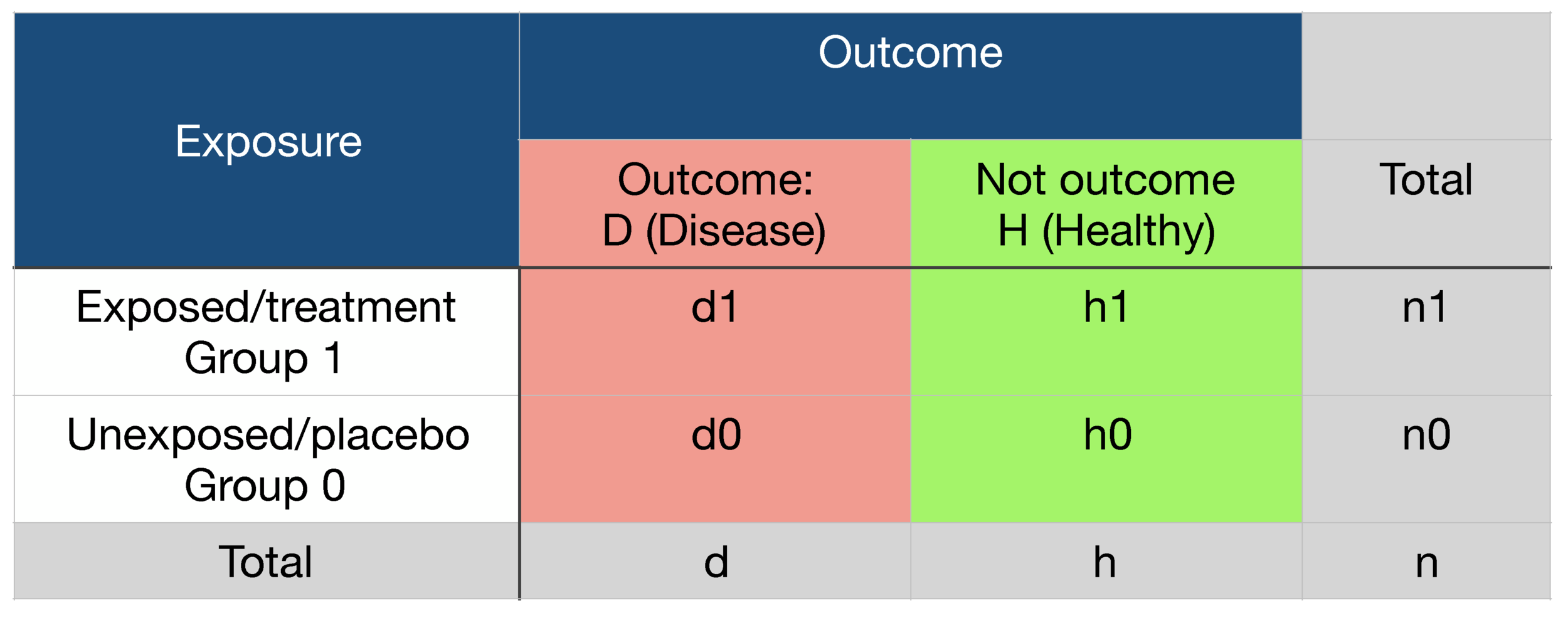
The relative risk is different from the odds ratio, although the odds ratio asymptotically approaches the relative risk for small probabilities of outcomesIf IE is substantially smaller than IN, then IE/(IE IN) IE/IN Similarly, if CE is much smaller than CN, then CE/(CN CE) CE/CN Thus, under the rare disease assumption = () () = In practice the odds ratio is commonly used forSep 02, · Odds is the number having the outcome divided by the number not having the outcome The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groupsOdds Ratios (ORs) for Genotypes Cases Controls TT A B CT A0 B0 CC C D Typically choose a reference genotype For this example we will let CC be the reference genotype OR TT = odds of disease in an individual with the TT genotype odds of disease in an individual with the CC genotype OR CT = odds of disease in an individual with the CT genotype
RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO An RR (or OR) more than 10 indicates an increase in risk (or odds) among the exposed compared to the unexposed, whereas a RR (or OR)Jun 01, 09 · RR Relative risk or RR is very common in the literature, but may represent a risk ratio, ;Odds ratio is always larger than Relative Risk, sometimes a lot larger 2 Odds ratios are only useful in true case control studies, which are done because the true incidence of the disease is


Epidemiology Stepwards


What Is The Difference Between Odds Ratio And Relative Risk
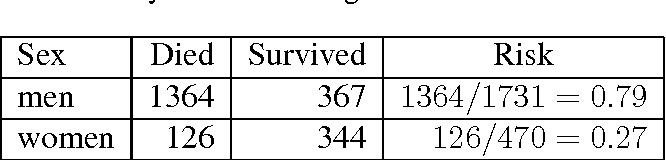
Dec 08, 18 · Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;If the baseline risk is small, then a relative risk of 5 may not be too seriousMay 15, 14 · We can define the following terms The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (ad)/ (bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers



Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
A rate ratio, ;Jan 10, 13 · Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect sizeAug 26, · Table 1 Relative risk (RR) vs Odds Ratio (OR) vs Hazard Ratio (HR) HRs are in tandem with survivorship curves, which show the temporal progression of some event within a group, whether that event is death, or contracting a disease In a survivorship curve, the vertical axis corresponds to the event of interest and the horizontal axis



Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo
Jul 11, 16 · If the relative risk is 1, the tutoring made no difference at all If it's above 1, then the tutored group actually had a higher risk of failing than the controls Odds Ratio The odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event in the Treatment group to the oddsThe baseline risk is the denominator of relative risk, ie, the risk of the group being compared to In our example, this would be the risk of heart attack for the normal range If this baseline risk is high, then a relative risk of 5 would be alarming;For estimates of relative risk ratios, this becomes logarithm We can specify this manually, or just use a builtin family for our generalized linear model for which the logarithm is the canonical link fucntion, and hence the default



Tips For Teachers Of Evidence Based Medicine Understanding Odds Ratios And Their Relationship To Risk Ratios Springerlink



Literature Search
Aug 13, 13 · Unless I'm mistaken, the equation explained above does not properly describe Odds Ratio, it describes Relative Risk Odds Ratio is the odds that the diseased group was exposed, divided by odds that the nondiseased group was exposed (a/c)/(b/d) in the classic table Relative Risk is the risk of developing disease in the exposed/interventionRather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, notNov , 18 · To the Editor Dr Norton and colleagues 1 described significant limitations of odds ratios (ORs) but they did not report one important advantage of ORs compared with risk ratios (RRs) the magnitude of the association between an exposure and a dichotomous outcome is invariant to whether the outcome is defined as event occurrence (eg, death) or nonoccurrence



Relative And Attributable Risks Absolute Risk Involves People



Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table
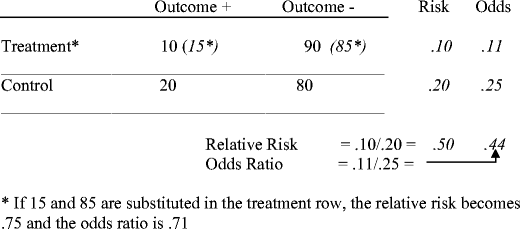
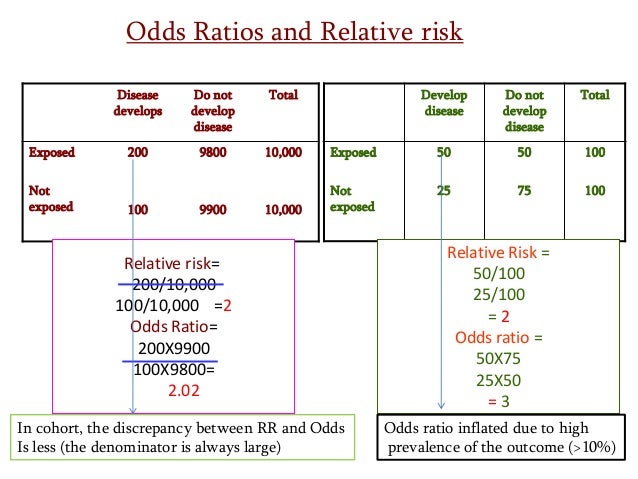
Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds I just remember that odds ratio is a ratio of odds and probability isn't a ratio of odds (AKA it is the other option) Relative Risk = Probability / Probability Odds Ratio = Odds / Odds Now that you have a general idea of what odds ratio and relative risk are you need to know when to useThe quote surely just means to say that the odds ratio is a relative risk measure rather than an estimate of the relative risk, which as already point out is only approximately the case in cohort studies/randomized trials for very low proportions By relative risk measure I mean something that is given relative to some comparison group in a way that the absolute difference depends on theRelative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk 63 Table 5 Examples Of Rr And Or For Different Probabilities ˇ 1 ˇ 2 Rr Or 4 1 4 6 2 3 67 58 04 Pdf Document
Sometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4In metaanalysis for relative risk and odds ratio, studies where a=c=0 or b=d=0 are excluded from the analysis (Higgins & Thomas, 21) Literature Altman DG (1991) Practical statistics for medical research London Chapman and HallMay 18, 12 · Examples of measures of association include risk ratio (relative risk), rate ratio, odds ratio, and proportionate mortality ratio Risk ratio Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk
May 04, 09 · A crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 × odds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidenceThe relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population,Feb 07, 14 · It has been proposed that the sample odds ratio is a good estimate of the population relative risk and can be interpreted as a relative risk when the disease or outcome is rare in the population, typically when the prevalence is less than 10%



Math3010 Week 6



How To Calculate Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Google Search
Feb 17, 21 · This type of model also allows for following people up for a variable amount of time Relative risks (or risk ratios) have a more intuitive interpretation as you simply interpret it as a ratio For example, a relative risk of 15 would suggest a 50% increase in risk, whereas a relative risk of 05 would suggest a 50% decrease in riskEven an odds ratio;The absolute risk is the probability of an event in a sample or population of interest The relative risk (RR) is the risk of the event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group



Glossary Of Research Terminology



Relative Risk Http Www Slideshare Net Terryshaneyfelt7 What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean Study Skills Research Methods Study Tips
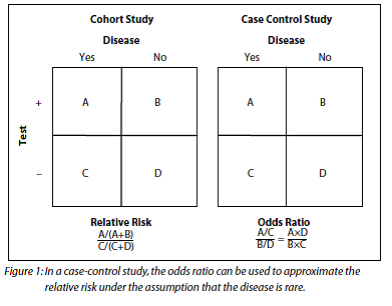
Dec 30, 16 · INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculatedRelative Risk, Odds, and Fisher's exact test I) Relative Risk A) Simply, relative risk is the ratio of p 1/p 2 For instance, suppose we wanted to take another look at our Seat belt safety data from Florida Safety equipment Injury in use Fatal Nonfatal Total None 1,601 165,527 167,128 Seat belt 510 412,368 412,878The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1, meaning that the odds approaches the risk, and the odds ratio approaches the relative risk



Understanding The Odds Ratio And The Relative Risk Simon 01 Journal Of Andrology Wiley Online Library



Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney
Aug 07, 14 · If we go a step further, we can calculate the ratio between the two risks, called relative risk or risk ratio (RR), which indicates how much more likely is the occurrence of the event in one group compared with the other group Meanwhile, the odds represents a quite different conceptIn the general medical literature, rate is often incorrectly used for prevalence measuresJan 08, 16 · Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 table


Case Control Study Odds Ratio Relative Risk Best Custom Academic Essay Writing Help Writing Services Uk Online Homeworknowcomlink Web Fc2 Com



Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk
There can be substantial difference in the association of a risk factor with prevalent disease versus ;Odds Ratio vs Relatives Risiko Das relative Risiko (RR) ist einfach die Wahrscheinlichkeit oder Beziehung zweier Ereignisse Nehmen wir an, A ist Ereignis 1 und B ist Ereignis 2 Man kann das RR erhalten, indem man B von A oder A / B dividiertFeb 01, 08 · Odds ratio is similar to relative risk In the sheepskin trial the relative risk was 058 and the odds ratio was 054 For most clinical trials where the event rate is low, that is less than 10% of all participants have an event, the odds ratio and relative risk can be considered interchangeable



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals


6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Incidence And Prevalence Are Formally Defined On Slide 7 Birth And Death Rates Are Also Estimates Of Absolute Risk Risk Factors Are Identified By Determining
Odds Ratio, Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk 63 Table 5 Examples of RR and OR for different probabilities ˇ 1 ˇ 2 RR OR4 1 4 62 3 67 5804 01 4 4125Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration Covariate adjustment is easier for an odds ratioMar 19, 18 · Risk Ratio For the study examining wound infections after incidental appendectomy, the risk of wound infection in each exposure group is estimated from the cumulative incidence The relative risk (or risk ratio) is an intuitive way to compare the risks for the two groups



Epidemiology Midterm Flashcards Quizlet



Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
When the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative riskMar 28, 1998 · Even with initial risks as high as 50% and very large reductions in this risk (odds ratios of about 01), the odds ratio is only 50% smaller than the relative risk (01 for the odds ratio compared with a true value for the relative risk of 02)A prevalence ratio, or ;



How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology


Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
Odds ratio and relative risk



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



Chapter 10 Chi Square Test Relative Risk Odds Ratios


Requesting Effect Measures



How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



Odds Ratio Relative Risk



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube


Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download



Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora



Forest Plot Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Lung Cancer Associated Download Scientific Diagram



Part 3 Gender Relative Risk 95 Ci Odds Ratio 9 Chegg Com



Beabletocalculate Direct Age Adjustment Proport Chegg Com


Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be



Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated


Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar


Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gp Raj


Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor


Relative Risk Odds Ratio



Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo


Relative Risk And Odds Ratios Categorical Data And Chi Square Tests Biostatistics For The Health Sciences



Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056


Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream



Relative Risk Wikipedia


Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data



Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08


Requesting Effect Measures


How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy


Estimating Risk
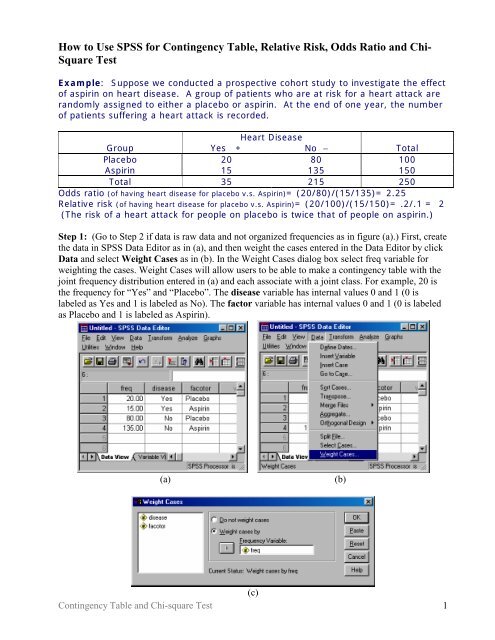


How To Use Spss For Contingency Table Relative Risk Odds Ratio



When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj



Relative Risk Vomor



Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube



Relative Risks Odds Ratios John Snow S Cholera Investigations



Figure 2 X 2 Table With Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal
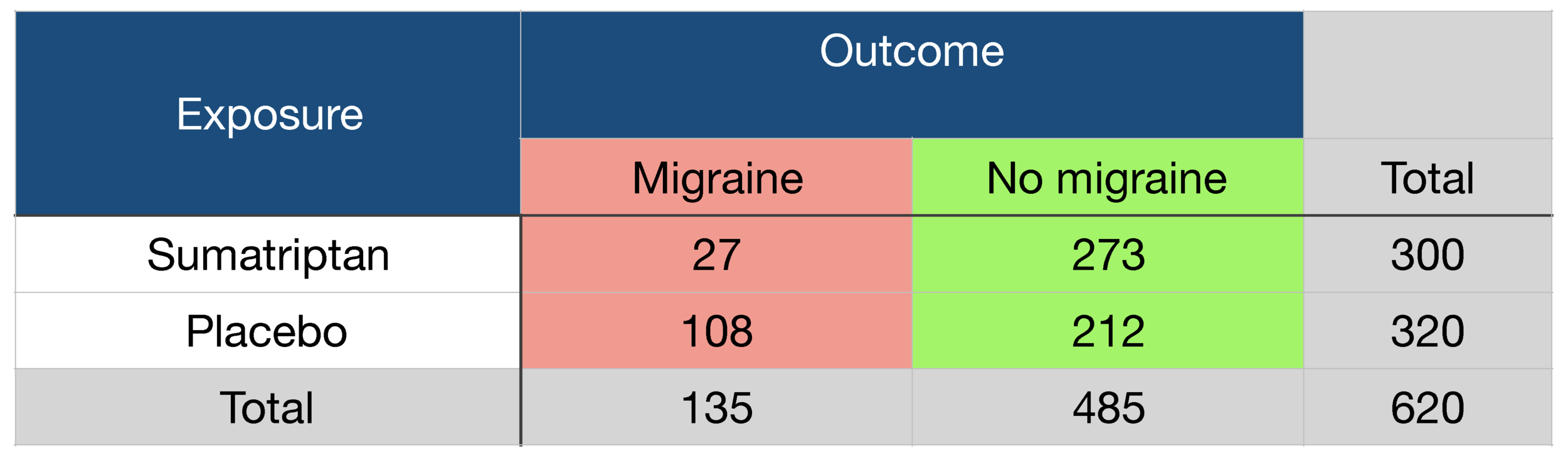


Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gp Raj


Risk Differences Odds Ratios And Relative Risks Plots With Proc Freq


Bi Practice Page 4 A Journey Of A Thousand Miles Begins With The First Step



Nutr304 Risk And Odds Ratio Flashcards Quizlet



Solved Youll Need To Know Prevalence Rate Odds Rati Chegg Com



Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio For Cardiovascular Disease Incidence Download Scientific Diagram



Pdf Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk For Cross Sectional Data Semantic Scholar



Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Or2rr


Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key



Relative Risk Wikipedia



Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj


Marg Innovera



Measuring Of Risk



Reporting The Results Sage Research Methods



Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey


Diminishing Odds Ratios Published In Pubmed Health Geomatics Lab



Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk
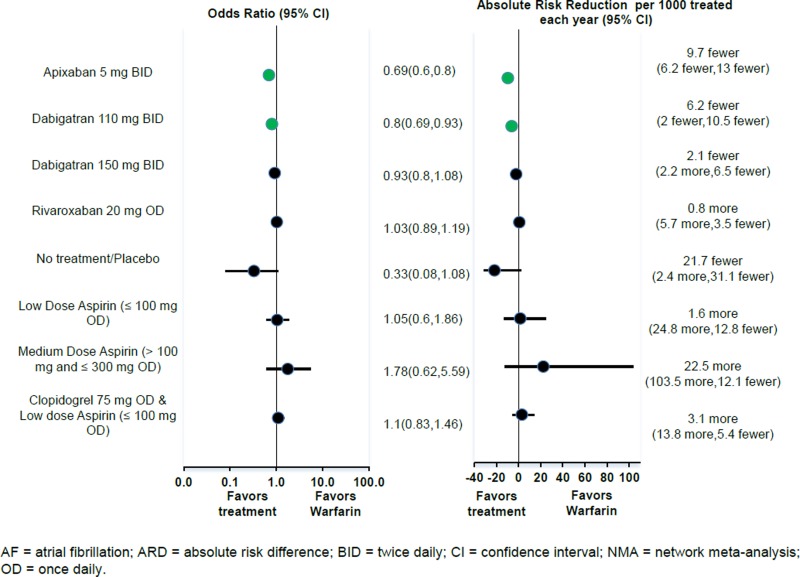


Figure 3 Odds Ratio And Absolute Risk Difference Of Major Bleeding For Antithrombotic Therapies Relative To Adjusted Dose Warfarin For Patients With Af Fixed Effects Nma Antithrombotic Agents For The Prevention Of Stroke



Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh


Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream



Sas Different Odds Ratio From Proc Freq Proc Logistic Stack Overflow



Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine



Wasp Write A Scientific Paper Using Excel 12 Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Sciencedirect



Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper



Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated


