This shortcut makes it is easier to solve problems using energy (if possible) rather than explicitly using forces More precisely, we define the change in gravitational potential energy ΔPE g to be ΔPE g = mgh , where, for simplicity, we denote the change in height by h rather than the usual Δ hThe force due to gravity on the surface is mg Therefore the work done by a system for relatively small hights "h" compered to the radius of the earth is W=mgh This is gravitational potential energy This is also equal to the work done by gravity as the object fallsThe Earth does POSITIVE work on the person, W= mgh

In This Qsn Wd By Gravity Shud Be Mg Sin Theta H Na So Why In The Aiats Video Physics Meritnation Com
W=mgh solve for h
W=mgh solve for h-Mgh = 0500 kg 980 m/s 2 100 m = 490 kg ⋅ m 2 /s 2 = 490 J mgh = 0500 kg 980 m/s 2 100 m = 490 kg ⋅ m 2 /s 2 = 490 J 728 Note that the units of gravitational potential energy turn out to be joules, the same as for work and other forms of energy As the clock runs, the mass is loweredSee the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (2 ratings) Previous question Next question Transcribed Image Text from this Question Question 5, chap 108, sect 5 part 1 of 1 10 points A weight lifter lifts a mass m at constant speed to a height h in time t How much



Ap Physics Unit 6 Chapter 13
The amount of work done is w = mgh, which is exactly equal to the amount of potential energy gained PE = mgh As the coaster begins to descend hill A, it loses potential energy (PE) and gains kinetic energy (KE), the energy of motionSolve for h a=1/2bh Rewrite the equation as Multiply both sides of the equation by Simplify Tap for more steps Cancel the common factor of Tap for more steps Cancel the common factor Rewrite the expression Multiply by Divide each term by and simplify Tap for more stepsMass through a displacement height h, and thus the work done in lifting the mass is W = Fs = (mg)h which must also equal its potential energy PE = mgh
W mgh (kg m s2 m = N m = J) w mgd cosT cos h d T h w mgd mgh d General formula w F dL ³ Line integral PV work (constant external pressure) m applies constant force F P A ( ) ( ) ext 12 F w mgh Fh Ah P V V A w P V V ext final initial Joules, or L Bar (1 L Bar = 100 J)Expert Answer If a body of mass m moves down from a height h, the forceof gravity or weight acts on the body through a displacement h Thus, work done by the force of gravity is W= ForceTextbooks define energy as "the ability to do work" and they define work as "overcoming resistance over a distance" For instance, if m is the mass of a brick, the force on it is mg and lifting it against gravity to a height h, against the pull of gravity, requires the performance of work W, with W = mgh
Kinetic Energy Imagine an object of mass "m" at rest at a height "h" If dropped, how fast will it be traveling just before striking the ground?1() Short Answer Questions A person jumps out of an airplane above the surface of the Earth, and falls a distance h a(4) The work done on the person by the Earth is Positive, Negative, Zero or Insu cient Information to Answer?In physics, for the formula Work = Mass x Gravity x Height



The Force Exerted By The Earth On A Particle Of Mass M A Distance R From The Centre Of The Earth Has The Magnitude Gme M R 2 Mgre 2 A Calculate The Work



Grade 11 Physics Nov 6 Gravitational Potential Energy
W = m g h cosθ Where the theta is the angle made when the body falls Solved Examples Example 1 A 15 kg box falls at angle 25 ∘ from a height of 10 m Determine the work done by gravity Solution Given Mass m = 10 kg, angle = The work done by gravity formula is given by, W = mgh cos θ W = 15 × 98 × 10× =15 × 98 × 10× = 1332 JMay 10, 10 · use the work equation W = mgh solve for h here Convert calories to joules 1 calorie = 4186 joules divide h by 15 feetYour question is absolutely meaningfultake mg in units of force kg m/s², mgh is in units of energy Kg m²/s² Newton's second law F=ma, a=g=981 m/s²now Work =W=F*s, in case of gravitation F=m*g and s could well mean height h The Work done equals the change of potential energy, therefore potential energy U=W=mgh



Pls Solve An Iron Nail Is Dropped From A Height H From The Level Of A Sand Bed If Physics Laws Of Motion Meritnation Com



Work Done Involving Friction And Other External Forces Physics Stack Exchange
Solve For each arm raise, you do work equal to W = mgh where h = 35 cm 4186 J 0(350 food cal) 1 food cal (0) (350) (4186 J) = N (mgh) 17 x (50 kg) (980 m/s2) (035 m) Reflect It is not reasonable to do this many repetitions in a single exercise session 741 Set Up Set % of the food energy (in joules) equal to the total work youThe total displacement (Δr) is simply the height h and the force will be the gravitational force F=mg We also know that the angle θ is zero, which means that cos(0°)=1 Inserting all of these into the formula for work (W=FΔrcosθ), we get that the work done by gravity on a falling object is W=mgh Work done by gravity on a falling object(12) $ \displaystyle W = mgh = 3000 \times \times $ = 701 megajoules Note This is a multipage article To navigate, use the dropdown lists



Ght H Leration Due To Gravity 8 9 8 Ms 2 M E Work Is Physics



Prove Potential Energy P E Mgh With Figure Brainly In
Nov 19, 09 · In physics, for the formula w=mgh, is mass in kilograms, and height in metres?Couldn't you solve for f from your xcoordinate forces (f=mgsin(theta)), and plug that straight into your work equation (W=fl)?Use your kinematics equations to get a formula for v 2 Since v o = 0, ∆ x = h, and a = g We can solve this for "gh" We're going to use this result later



Phys111f15mt2topics Topics For Midterm 2 Studocu
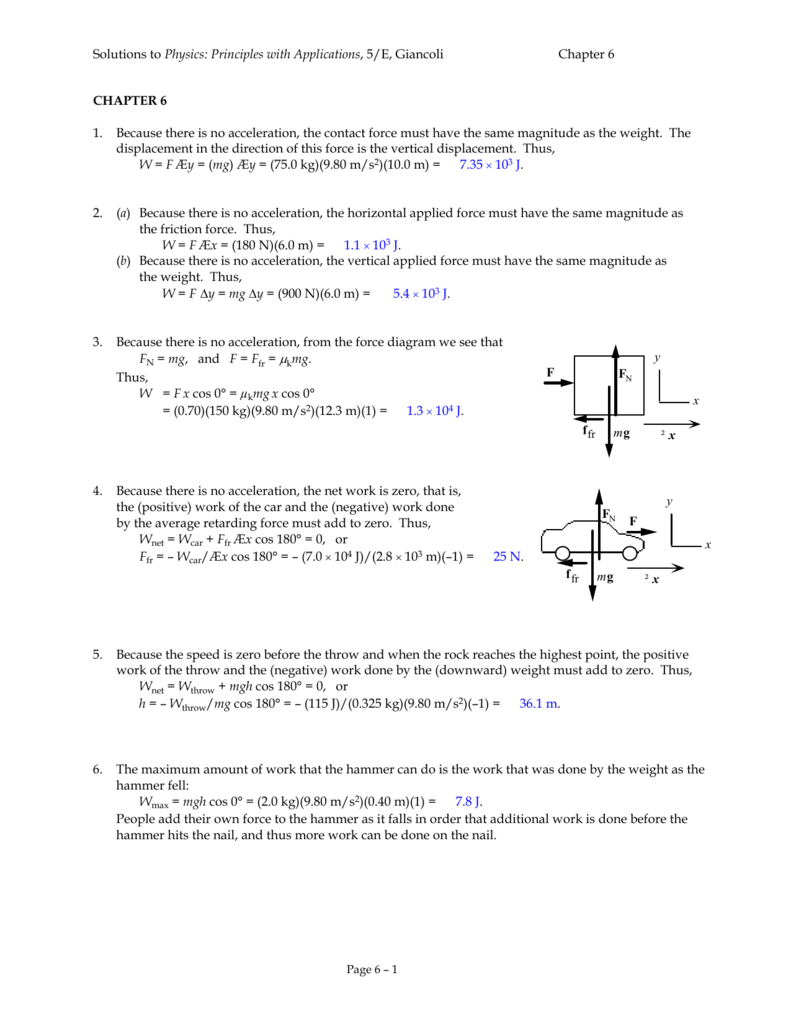


Ch 6 Physics Answers
W = Mgh 4 W = Mgh 5 W = Mg This problem has been solved!(c) We don't know the max height Denote it as H, and it is measured above the equilibrium point of the spring So ∆U g = mg(H 04 m), where m = 85 kg The answer in the back of the book reflects our knowledge that the change in U g is equal toH h=0 PHY 700 Energy and Work J Hedberg 21 Page 4 Updated on If these are the only two types of energy in the system, then we have a very special situation We can define the total mechanical energy energy of the system as the kinetic potential



Answers
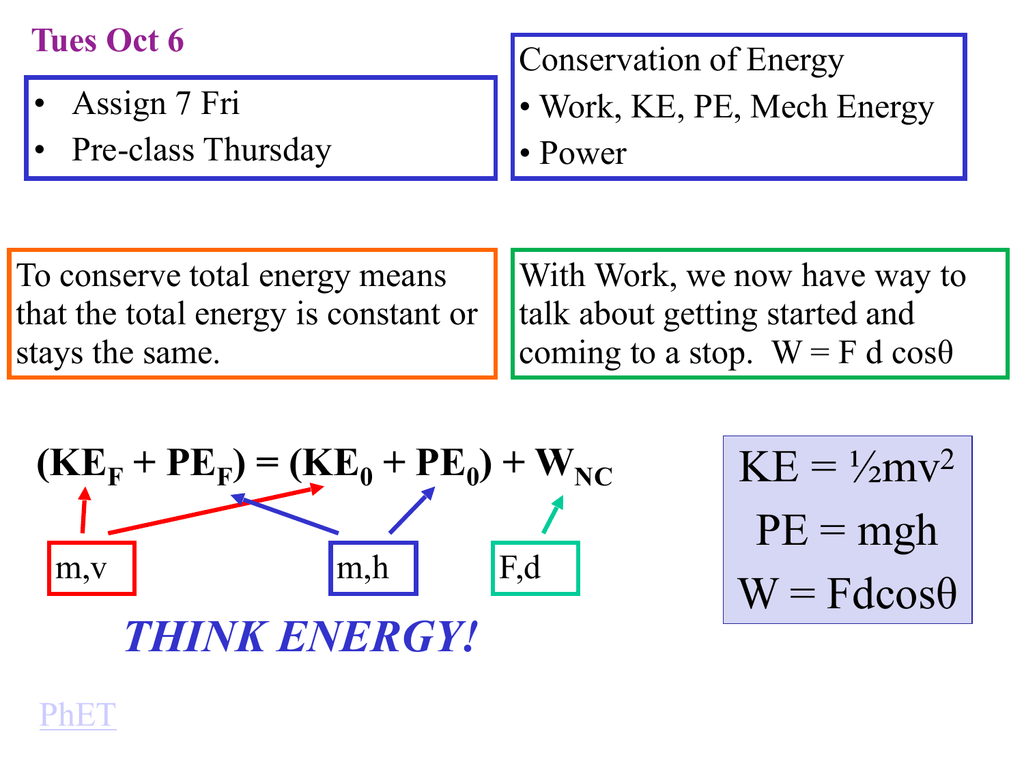


Think Energy Ke Mv2 Pe Mgh W Fdcos8
Mar 14, 09 #2 Dale Mentor Insights Author (height) The work done equals the change of potential energy So potential energy U = W = mgh Mar 14, 09 #6 cragar 2,544 3 i thought work was the change in kinetic energy and work is the integral of F*s Mar 14, 09 #7Isn't it somewhat repetitive to solve for the coefficient of kinetic friction, to plug back in to solve for friction, to calculate work?These principles allow us to solve problems without worrying too much about the details of a process W=mgh to lift the barbell so mgh=Ef The energy of a mass is increased by an amount mgh when it is raised by a height "h" Slide 32 / 112 Gravitational Potential Energy



Grade 11 Work Energy Physics Need Help Understanding How To Solve Work And Energy Practice Problems Physicsstudents



Solved Solve The Question Using The Laws Written On The Chegg Com
Free solve for a variable calculator solve the equation for different variables stepbystep This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experienceW =mgh = × ×h = This can easily be solved for h to yield And, since we have 3 meters per floor, we just divide by three to find that the total number of floors is slightly over 28 Scary!WORK Work is the energy transferred into orout of a system through the action of a force Work done againstgravity can be found using the equation Work equals Forcetimes heightor W = Fh Since F = mg we can use the equation W = mgh (m =mass, g = gravity, or 981m/s² and h = height) Lets try an example



Conservation Of Energy Video Khan Academy



Solved Av Total Distance Average Speed Elapsed Time Ax Chegg Com
H Vel V PE mgh KE ½ mv2 TE PEKE @Top @Intermediate level @Bottom 0 Note Start by calculating the Total Energy at the top –this is the size of the energy "pool" for distribution as the object moves lowerThis change in velocity is caused by the work done by gravitational force We know the change in velocity, and hence the change in kinetic energy of the ball, and can calculate its maximum height from this W = ΔK mgh = mvf2 mvo2 But vf = 0 , and the masses cancel, so h = = = 319 mNow we had better solve for the maximum upward acceleration of the jumper It occurs at the maximum stretch of the bungee cord, as that is when the stretch distance is the greatest If the elevator cable should happen to break at a height of h above the top of the spring, W = mgh, so P = W/t = mgh/t = (47,000 people)(70 kg/person)(98 N
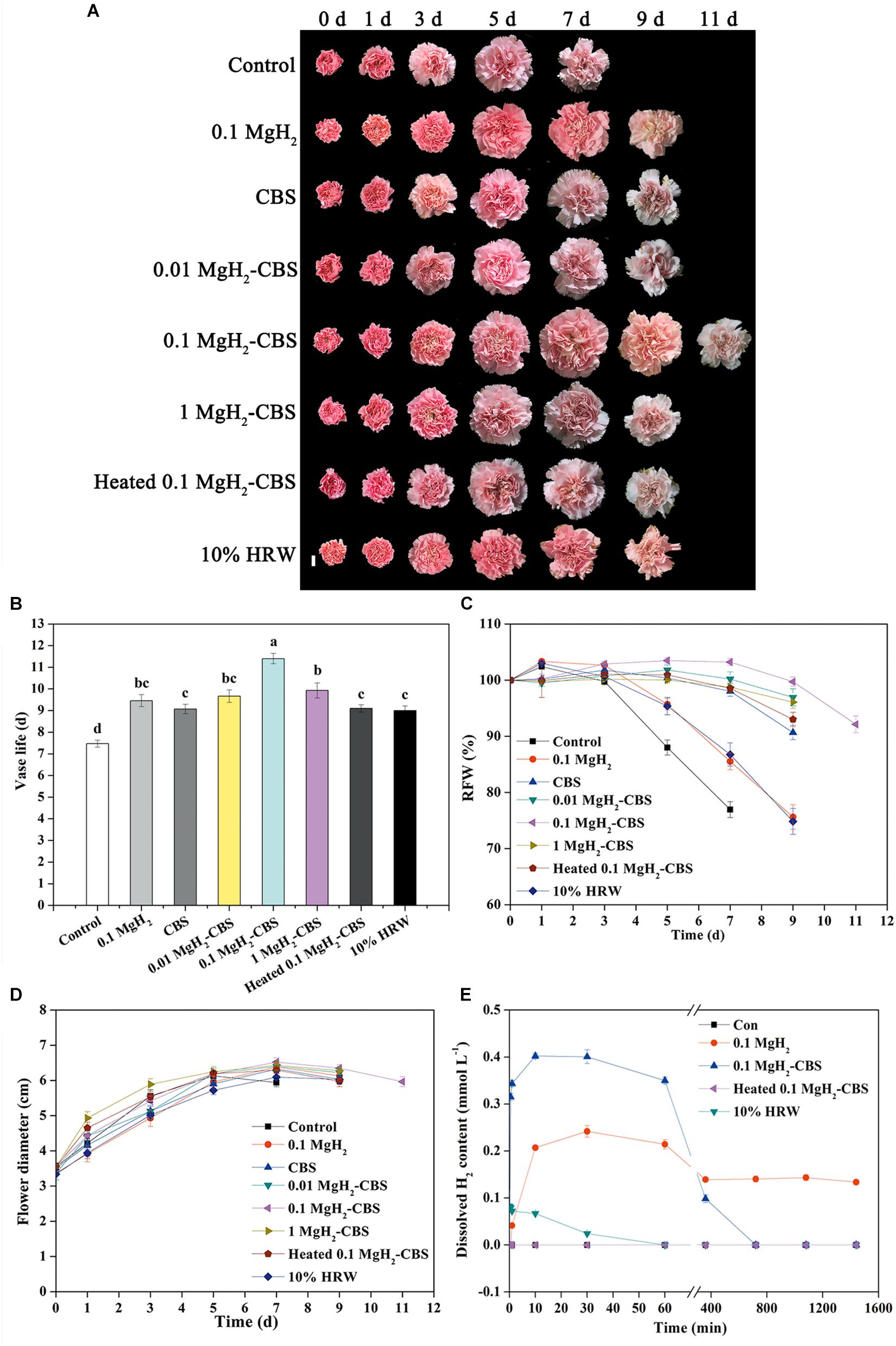


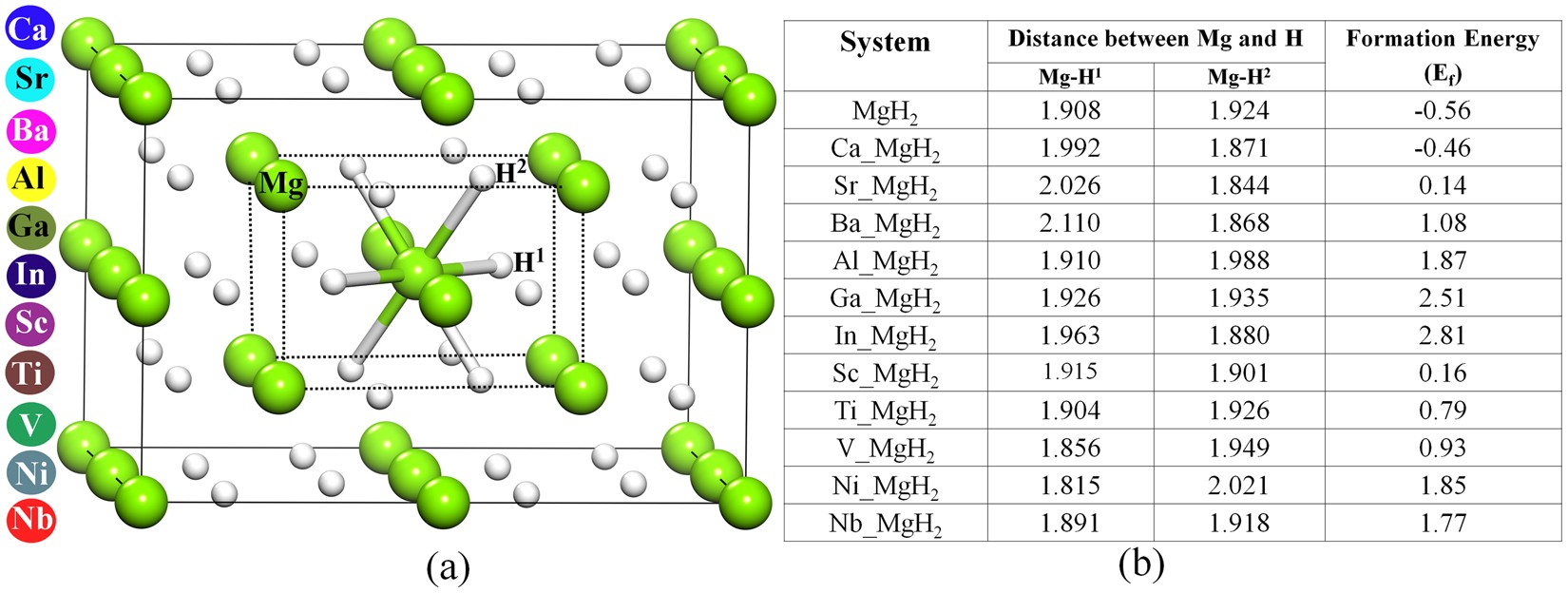
Frontiers Magnesium Hydride Mediated Sustainable Hydrogen Supply Prolongs The Vase Life Of Cut Carnation Flowers Via Hydrogen Sulfide Plant Science



Potential Energy Equation Mgh Page 1 Line 17qq Com
H, the work done by the gravitational force is always equal to mgh • W = mgh • An object near the Earth's surface has a potential energy (PE) that depends only on the object's height, h • The PE is actually a property of the Earth object system Section 63Sep 04, · (v) Work done by the force of gravity on a particle of mass m is given by W = mgh where, g is acceleration due to gravity and h is height through which the particle is displaced (vi) Work done in compressing or stretching a spring is given by W = \(\frac{1}{2}\)kx² where, k is spring constant and x is displacement from mean positionApply the ideal gas law to solve problems in chemistry Key Takeaways Key Points An ideal gas exhibits no attractive forces between particles In the ideal gas equation, both pressure and volume are directly proportional to temperature Key Terms ideal gas constant R = 145 J·mol1·K1;



3 Find Speed Ofend A When It Is At Point B A 25 1 H In 9 0 2gh In A 6 Van 1 2 A P3sh 1 4 14 Find Max Kinetic Energy Of Chain Before End



Check The Correctness Of Equation 1 2mv2 Mgh Using Dimensional Analysis Method Brainly In
Problem Solving and Program Design in C A collection of C programs I wrote to solve problems in Problem Solving and Program Design by Jeri Hanly and Eliot Kaufman Overview of C Taxi Fare Calculator /* Write a program that calculates taxi fare at a rate of $150 per mileRearrange the formula Ep = mgh, to find hThese principles allow us to solve problems without worrying too much about the details of a process W=mgh to lift the barbell so mgh=Ef The energy of a mass is increased by an amount mgh when it is raised by a height "h" Slide 31 / 112 Gravitational Potential Energy



Answered 1 Uinitial Kfinal Mgh Mv Iw 2 Or Bartleby


Solved Solve Using The Principles Of Energy Conservation Write The Kinetic Potential And Total Energy Of A Baseball Having A Mass Of 0 145kg Held Course Hero
Gravitational potential energy is one type of potential energy and is equal to the product of the object's mass (m), the acceleration caused by gravity (g), and the object's height (h) as distance from the surface of the ground (the body) In this example, a 3 kilogram mass, at a height of 5 meters, while acted on by Earth's gravity would have Joules of potential energy, PE = 3kgW mgh, for g 15 PV nRT, for V 16 G F D, for D 17 6t 62s (3t 42s), for t 18 3c 5d 7d 6c, for d 19 Standardized Test Practice Four ninths of a number c increased by 4 is 18 less than one eighth times another number d Solve for c A c 3 9 2 d 31 1 2 B c 7 4 2 d 7 4 2 C c 3 9 2 d 49 1 2 D c 7 4 2 d 31 1 2 1 2 4 3 n 2 Solving Equations andAnswer to Calculate the mass of glucose metabolized by a 5 kg person in climbing a mountain with an elevation gain of 1230 m Assume that the



A Solid Sphere Rolls Down A Roof How To Solve Physics Problems



Vertical Springs And Energy Conservation Video Khan Academy
Mass through a displacement height h, and thus the work done in lifting the mass is W = Fs = (mg)h which must also equal its potential energy PE = mghMar 15, 09 · Radioactive molecules may help solve mystery of missing antimatter;That can of Coke would fuel nearly three trips up the Empire State Building!



Giancoli 6th Edition Problem Solutions Chapter 6



Htpibreview Ch6 P Mgh T Example Youtube
College"Physics" Student"Solutions"Manual" Chapter"7" " 58" " Solution" Given m =800 kg, h = 0600 m, and d = m"" Find"net FU sing"W = Fd and"the"workSenergy"theorem"gives"W = F j d = mgh" 3136 10 N m (800 kg)(980 m/s2)(0600) 4 = = = × d mgh F " N mThe work done to climb a vertical height h is W = mgh We solve for h W 21 X 106J _ h = = rr = 3600 m mg (60 kg) (980 m/s2) This is a huge elevation change (over 11,000 ft) NOTE The human body does not transform food energy with 100% efficiency—it is more like % efficientI need to solve this question a) m=0 g, h=0039 m Find W=mgh b) We have a parallelogram P(kPa) Vs V (m^3) P is from to 1036 kPa And V is from 132 to 162m^3 Calculate the area enclosed by the PV diagram Show your calculations with units Hints Careful use of appropriate SI (MKS) units is essential



In This Qsn Wd By Gravity Shud Be Mg Sin Theta H Na So Why In The Aiats Video Physics Meritnation Com



Solve For H P Mgh Answer Choices H P Mg H Pg M H P Mg H P Mg
All that is left is to solve for the unknown part of KE F Work – Energy concepts Let the distance over which weight acts be height h So work done by gravity W = mgh Since work is equivalent to energy, then mgh is equal to what we call the gravitational potential energy DrMay 31, 11 · diatnce, D = height, h, Thus, W = mgh = 72x10^9 x 98x18 = 32x10^7 >=====< ANSWERSep 17, 08 · It is better to solve the equation for h first before plugging in any numbers So, the equation is W = mgh Solve for h by dividing both sides by mg h



Solved The First Screen Shot Is The Example That Is Given Chegg Com



Error Using Mgh Intro To Physics Youtube
Step 1 Enter the mass, acceleration due to gravity, and height in the input field Step 2 Now click the button "Calculate Potential Energy" to get the Energy Step 3 Finally, the potential energy of the body will be displayed in the output field



Chapter Seven Energy 7 1 Energy And Systems Ppt Download



Conservation Of Energy Ppt Download



Solution



Chapter 11 H 5m Mgh Mv Iw 2 E F E I V 4 3 G H H M S2 8m 5m 6 26m S W V R 6 Pdf Free Download



Solved Average Speed Tota Distance Elapsed Time A Av Di Chegg Com



Work And Conservation Of Energy Pdf Free Download



Pdf Conceptual Problem Solving In High School Physics Semantic Scholar
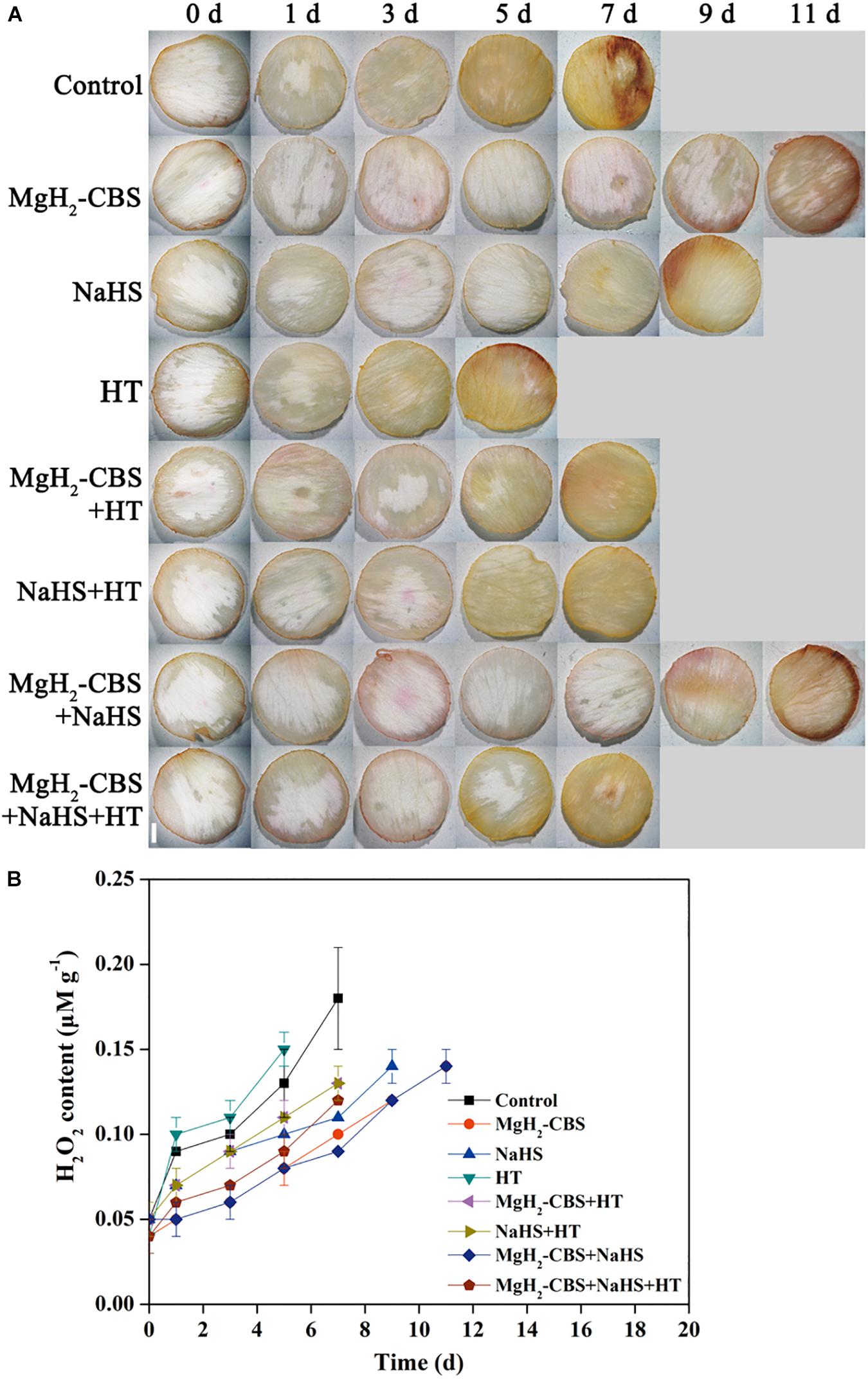


Frontiers Magnesium Hydride Mediated Sustainable Hydrogen Supply Prolongs The Vase Life Of Cut Carnation Flowers Via Hydrogen Sulfide Plant Science



Ppt Work Power Energy Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Htpib06c Calculating Gravitational Potential Energy Using Ep Mgh Youtube



Hw12 Interactions Long Homework Solution 12 Solution For Homework 12 Studocu



Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 4 Work And Energy Free Pdf



Ch 6 Work And Enery



Ppt Chapter 15 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



A Helicopter Lifts A 72 Kg Astronaut 15 M Vertically From The Ocean By Means Of A Cable The Acceleration Of The Astronaut Is Frac G 10 How Much Work Is Done On



Ap Physics Unit 6 Chapter 13



Answered The Equation Used To Solve For Bartleby



Let Us Consider An Equaiton 1 2 Mv 2 Mgh Where M Is The Mass Of The Body Upsilon Its Youtube


Screening Based Approach And Dehydrogenation Kinetics For Mgh 2 Guide To Find Suitable Dopant Using First Principles Approach Scientific Reports



Test Bank For Applied Physics 11th Edition By Ewen Ibsn By Grewau Issuu


